Melanoma Symptoms ABCDE: Detecting Skin Cancer Early
Melanoma Symptoms ABCDE: Detecting Skin Cancer Early
Learn how to spot melanoma symptoms using the ABCDE method. Protect your skin and health with early detection.

Melanoma Symptoms
Introduction
Skin cancer is a growing concern worldwide, and melanoma is one of its most dangerous forms. Detecting melanoma early can be life-saving. In this article, we'll explore the ABCDE method, a reliable way to identify potential melanoma symptoms. By understanding these signs, you can take proactive steps to protect your skin and overall health.
Understanding Melanoma
Melanoma is a type of skin cancer that begins in the melanocytes, the cells that produce melanin, the pigment responsible for your skin's color. It can occur anywhere on the body, and early detection is crucial for successful treatment.
Melanoma: The Dangerous Skin Cancer
Melanoma is a type of skin cancer that originates in the melanocytes, the pigment-producing cells responsible for giving color to our skin, hair, and eyes. Unlike other forms of skin cancer, melanoma is particularly dangerous because it has a higher tendency to spread to other parts of the body, a process known as metastasis. Early detection and treatment are critical for improving the prognosis and preventing the spread of melanoma.
Risk Factors for Melanoma
Understanding melanoma starts with recognizing the risk factors that can make someone more susceptible to this type of cancer:
- UV Exposure: The primary risk factor for melanoma is exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or artificial sources like tanning beds. Prolonged or intense UV exposure can damage the DNA in skin cells, increasing the risk of melanoma.
- Fair Skin: People with fair skin, light hair, and light-colored eyes are generally at a higher risk because they have less melanin, which provides some natural protection against UV radiation.
- Family History: A family history of melanoma can increase an individual's risk, suggesting a genetic predisposition.
- Moles: Having a large number of moles or atypical (dysplastic) moles can also be a risk factor. Changes in these moles are often a warning sign of melanoma.
Melanoma Staging
Melanoma is typically categorized into stages based on its size, depth, and whether it has spread to nearby lymph nodes or distant organs. The staging system helps determine the severity of the disease and guides treatment decisions.
- Stage 0: Melanoma in situ, where the cancer is limited to the top layer of the skin and hasn't invaded deeper layers.
- Stage I and II: Melanoma is still localized to the skin but may have penetrated deeper layers.
- Stage III: The cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes but hasn't reached distant organs.
- Stage IV: Melanoma has metastasized to distant organs, making it more challenging to treat.
- Early Detection and Prevention
Given the aggressiveness of melanoma, early detection is paramount. Regular self-examinations of your skin, using methods like the ABCDE rule, can help identify potential melanoma symptoms. If you notice any changes in moles or skin lesions, consult a dermatologist promptly.
Preventing melanoma includes:
- Sun Protection: Using sunscreen with a high SPF, wearing protective clothing, and seeking shade during peak sun hours can reduce UV exposure.
- Avoiding Tanning Beds: Artificial UV radiation from tanning beds is a significant risk factor; it's best to avoid them.
- Regular Skin Checkups: Routine skin exams by a dermatologist can help detect melanoma in its early stages.
Understanding melanoma involves recognizing its risk factors, stages, and the importance of early detection and prevention. By being aware of these factors and taking proactive steps to protect your skin, you can reduce your risk and ensure a better chance of successful treatment if melanoma is detected.
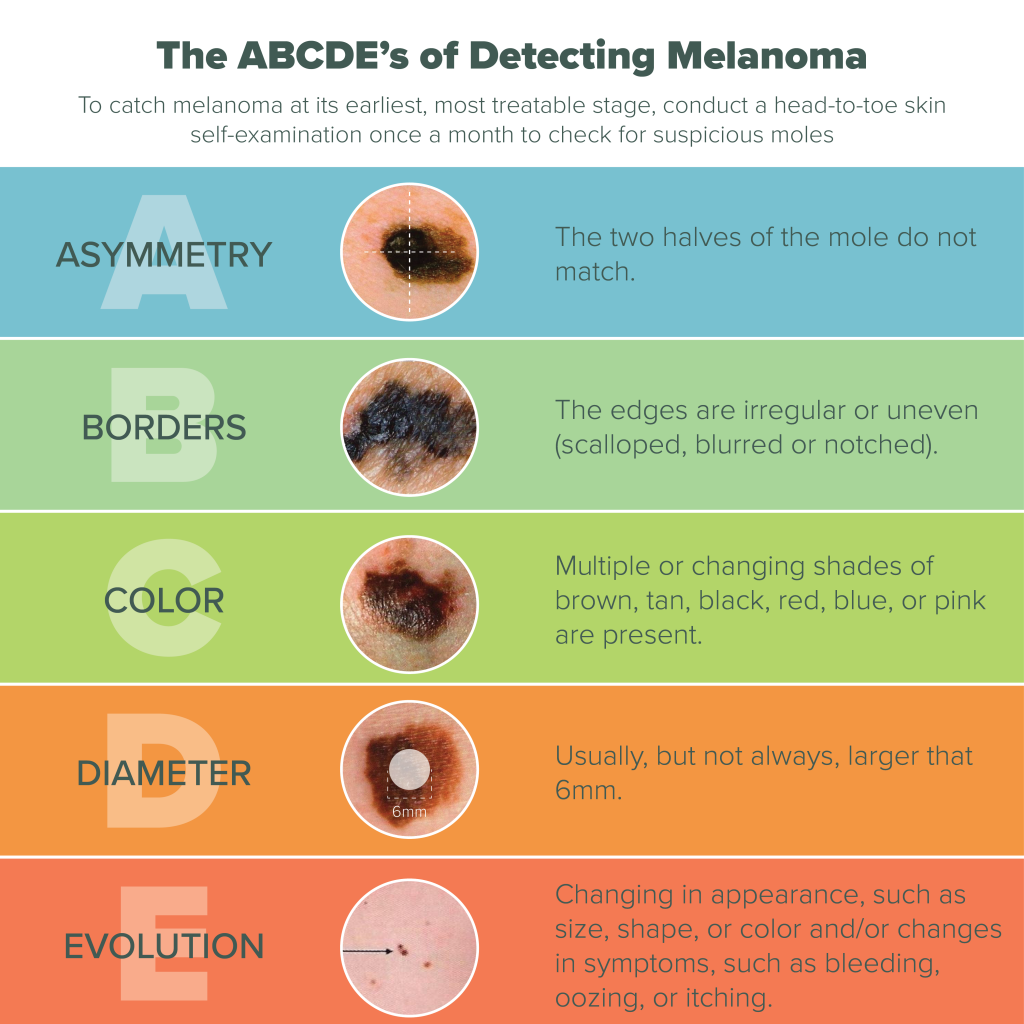
The ABCDEs of Melanoma Symptoms
To identify potential melanoma, dermatologists use the ABCDE rule:
A: Asymmetry
Healthy moles are typically symmetrical. If you draw an imaginary line through the center, both halves should look the same. In melanoma, moles often appear asymmetrical, with one half differing from the other.
B: Border
Check the borders of your moles. Melanoma lesions tend to have irregular, poorly defined, or jagged borders. Healthy moles usually have smooth, even edges.
C: Color
Pay attention to the color of your moles. Melanoma may display various colors within the same mole. Shades of brown, black, red, blue, or white can be concerning.
D: Diameter
Melanoma lesions are often larger than the eraser on a pencil, which is roughly 6mm in diameter. If a mole grows in size, it should be examined by a dermatologist.
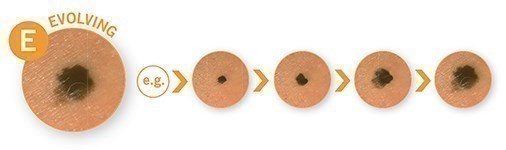
E: Evolution
Be vigilant about changes in your moles over time. If you notice a mole evolving in size, shape, color, or elevation, consult a healthcare professional.
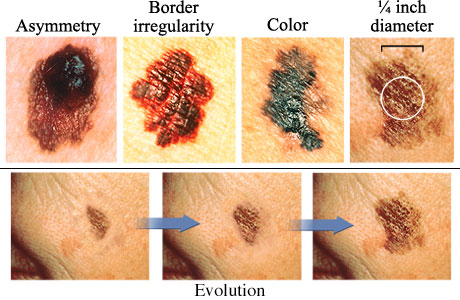
Identifying Melanoma Through Visual Inspection
Visual inspection plays a crucial role in melanoma detection. Regularly examine your skin using the ABCDE method. Here's how you can perform a self-examination:
- Asymmetry: Look for moles that are not symmetrical. If one half doesn't match the other, it could be a sign of melanoma.
- Border: Examine the borders of your moles. Are they irregular or poorly defined?
- Color: Note the color of your moles. Multiple colors or unusual shades should raise concerns.
- Diameter: Measure the diameter of your moles. If they are larger than 6mm (about the size of a pencil eraser), consult a dermatologist.
- Evolution: Keep track of any changes in your moles. Document alterations in size, shape, color, or elevation.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Can melanoma develop on any part of the body?
Yes, melanoma can develop on any part of the body, including areas that receive minimal sun exposure. It's important to check your entire skin regularly.
Q2: Is melanoma a common form of skin cancer?
While melanoma is less common than other types of skin cancer, it is more likely to spread and become life-threatening if not detected early.
Q3: Are all moles potentially cancerous?
No, most moles are harmless. However, it's crucial to monitor them for changes using the ABCDE method.
Q4: Is melanoma hereditary?
While genetics can play a role, melanoma is primarily linked to UV exposure. Protecting your skin from the sun is key to prevention.
Conclusion
Early detection is the best defense against melanoma. By familiarizing yourself with the ABCDE method and performing regular self-examinations, you can spot potential melanoma symptoms and seek prompt medical attention if needed. Remember that protecting your skin from harmful UV rays through sunscreen and protective clothing is also essential in preventing melanoma. Prioritize your skin health and reduce your risk of melanoma through vigilance and sun-safe practices.
Learn about symptoms of melanoma. Most have a black or black blue area.
3 Ways To Use ABCDE When Checking Moles
When it comes to monitoring your skin for potential melanoma symptoms, the ABCDE method is a valuable tool. This method helps you identify irregularities in moles or skin lesions that could be signs of skin cancer. Here are three ways to use ABCDE when checking your moles:
1. Asymmetry (A)
Normal Moles: Healthy moles are typically symmetrical, meaning they look the same on both sides when you draw an imaginary line through the center. This symmetry indicates that the mole is stable and less likely to be cancerous.
Using ABCDE: To use the "A" in ABCDE, examine your mole for any noticeable asymmetry. If one half of the mole doesn't match the other, it could be a cause for concern. An asymmetrical mole may be a potential indicator of melanoma.
2. Border (B)
Normal Moles: Healthy moles generally have smooth, even borders. The edges of the mole should be well-defined and not irregular or jagged.
Using ABCDE: For the "B" in ABCDE, closely inspect the borders of your mole. If you notice that the borders are uneven, poorly defined, or appear jagged, it's essential to get the mole examined by a healthcare professional. Irregular borders can be a sign of melanoma.
3. Color (C)
Normal Moles: Most normal moles have a consistent color throughout. They are typically one shade of brown, tan, or black.
Using ABCDE: The "C" in ABCDE involves observing the color of your mole. Be cautious if you notice multiple colors within the same mole or if the mole exhibits unusual shades like red, blue, or white. These variations in color could be indicative of melanoma.
Remember that while the ABCDE method is a valuable self-assessment tool, it's not a substitute for professional medical advice. If you notice any of these ABCDE signs or any other concerning changes in your moles, it's crucial to consult a dermatologist or healthcare provider for a thorough evaluation. Early detection is key to successful melanoma treatment, so don't hesitate to seek medical attention if you have any doubts about your skin's health.
The first sign is often a new mole or a change in the appearance of an existing mole.
- New Moles: If you suddenly notice a new mole on your skin, especially in areas that receive sun exposure, it should raise a flag. While not all new moles are cancerous, any new growth on your skin warrants attention and should be examined by a dermatologist.
- Changes in Existing Moles: Equally important is keeping an eye on existing moles. If a mole you've had for a long time starts to evolve in any way, such as changing in size, shape, color, or elevation, it could be a sign of melanoma. Even subtle changes should not be ignored.
Melanoma symptoms ABCDE
Signs of melanoma include new spots on the skin or a change in size shape or color of an existing mole. This skin cancer can form on your skin scalp genitals and even under a nail melanoma the deadliest skin. The abcde method may help you determine.
The most important warning sign for melanoma is a new spot on the skin or a spot that is changing in size shape or color. Melanoma is the most serious type of skin cancer. Signs and symptoms patients with melanoma.
Melanoma also known as malignant melanoma is a type of cancer that develops from the pigment containing cells known as melanocytes. Learn what you should look for. Even if you have carefully practiced sun safety all summer its important to continue being vigilant about your skin in fall winter and beyond.
Read about the signs and symptoms of melanoma. Get information on melanoma skin cancer signs diagnosis treatment prognosis and symptoms. Learn the abcde of what to watch for and treatment options.
Melanocytes are cells that produce melanin the dark pigments responsible for the color of skin. Melanomas typically occur in the. Learn about staging early detection treatment side effects.
Symptoms of melanoma include a new mark or spot on the skin and a mole or spot that changes size shape color or height. Definition melanoma is a malignant tumor of melanocytes.
Skin Cancer Information That Could Save Your Life Skin Cancer
Melanoma Infographic Copy Johnson County Dermatology
 Melanoma Treatment U S Dermatology Partners
Melanoma Treatment U S Dermatology Partners
 Spotting Early Signs Of Melanoma Everyday Health
Spotting Early Signs Of Melanoma Everyday Health
Melanoma Causes Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Prevention
 Signs And Symptoms Understanding Macmillan Cancer Support
Signs And Symptoms Understanding Macmillan Cancer Support
 Abcde Rule Melanoma Rtwskin Aesthetics Clinic
Abcde Rule Melanoma Rtwskin Aesthetics Clinic
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-586031566-5aeb11cdfa6bcc00362cf449.jpg) Melanoma Symptoms Signs And Abcd Mnemonic
Melanoma Symptoms Signs And Abcd Mnemonic
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/skin-cancer-symptoms-5b0d84a7119fa8003747e2cb.png) Skin Cancer Signs Symptoms And Complications
Skin Cancer Signs Symptoms And Complications
Melanoma Dr Farrah Cancer Center
 What To Look For Abcdes Of Melanoma American Academy Of Dermatology
What To Look For Abcdes Of Melanoma American Academy Of Dermatology
 Signs And Symptoms Understanding Macmillan Cancer Support
Signs And Symptoms Understanding Macmillan Cancer Support
Internal Melanoma Symptoms How To Recognize Them

