Malignant Melanoma Symptoms And Signs: Understanding the Warning Signals
Malignant Melanoma Symptoms And Signs: Understanding the Warning Signals
Introduction
Malignant melanoma, a form of skin cancer, is becoming increasingly prevalent worldwide. It's crucial to recognize the symptoms and signs of this potentially life-threatening condition early on to seek prompt medical attention. In this article, we'll delve into the intricate details of malignant melanoma, covering its symptoms and signs comprehensively.

What Is Malignant Melanoma?
Before we delve into the symptoms and signs, let's first understand what malignant melanoma is. This type of skin cancer develops in melanocytes, the cells responsible for producing pigment in your skin.
Malignant melanoma is a type of skin cancer that originates in the melanocytes, which are the cells responsible for producing melanin, the pigment that gives color to our skin, hair, and eyes. These cells are located in the epidermis, the topmost layer of the skin. Melanoma occurs when these melanocytes begin to grow uncontrollably and become cancerous.
Here's a more detailed breakdown of the key aspects of malignant melanoma:
1. Origin of Melanoma:
Melanoma begins when the DNA in melanocytes is damaged or mutated. This damage can be caused by various factors, including exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds, genetic predisposition, or a combination of these factors.
When the DNA damage occurs, the melanocytes can lose their ability to regulate their growth, leading to the formation of cancerous cells.
2. Types of Melanoma:
There are several subtypes of melanoma, including superficial spreading melanoma, nodular melanoma, lentigo maligna melanoma, and acral lentiginous melanoma, among others. Each subtype may have unique characteristics and patterns of growth.
Superficial spreading melanoma is the most common subtype and often appears as irregularly shaped moles that spread horizontally on the skin's surface before penetrating deeper layers.
3. Metastasis:
What makes malignant melanoma particularly dangerous is its potential to metastasize or spread to other parts of the body. This can happen when cancer cells break away from the primary tumor and travel through the bloodstream or lymphatic system to establish new tumors in distant organs like the lungs, liver, brain, or bones.
Once melanoma has metastasized, it becomes much more challenging to treat and can be life-threatening.
4. Risk Factors:
Several risk factors increase the likelihood of developing malignant melanoma. These include a history of severe sunburns, excessive UV exposure, having many moles or atypical moles, a family history of melanoma, and having fair skin, light hair, and blue or green eyes.
It's important to note that while UV exposure is a significant risk factor, melanoma can also occur in areas of the body that are not typically exposed to the sun.
5. Early Detection and Prevention:
Early detection of melanoma is crucial for successful treatment and a better prognosis. Regular skin self-examinations and professional skin checks by a dermatologist can aid in early detection.
Preventative measures include sun protection, such as wearing sunscreen, protective clothing, and avoiding tanning beds. Additionally, individuals with a family history of melanoma may benefit from genetic counseling.
Malignant melanoma is a form of skin cancer that arises from the uncontrolled growth of melanocytes. It is characterized by various subtypes and has the potential to spread to other parts of the body if not detected and treated early. Understanding the risk factors and taking preventive measures, along with regular skin examinations, are essential steps in managing the risk of malignant melanoma and promoting skin health.

Recognizing the Signs
1. Irregular Moles (H1)
One of the earliest signs of malignant melanoma is the presence of irregular moles. Keep an eye out for moles that have uneven borders, irregular shapes, or varying colors.
2. Changes in Mole Size (H2)
If you notice a mole increasing in size or thickness, it could be an indicator of melanoma. Any mole that grows significantly should be evaluated by a dermatologist.
3. Darkening of Existing Moles (H2)
Moles that darken over time should raise concern. Melanoma can cause existing moles to change color, becoming darker or developing shades of black.
4. New Moles (H2)
The sudden appearance of new moles, especially after the age of 30, is suspicious. These new moles should be examined by a healthcare professional.
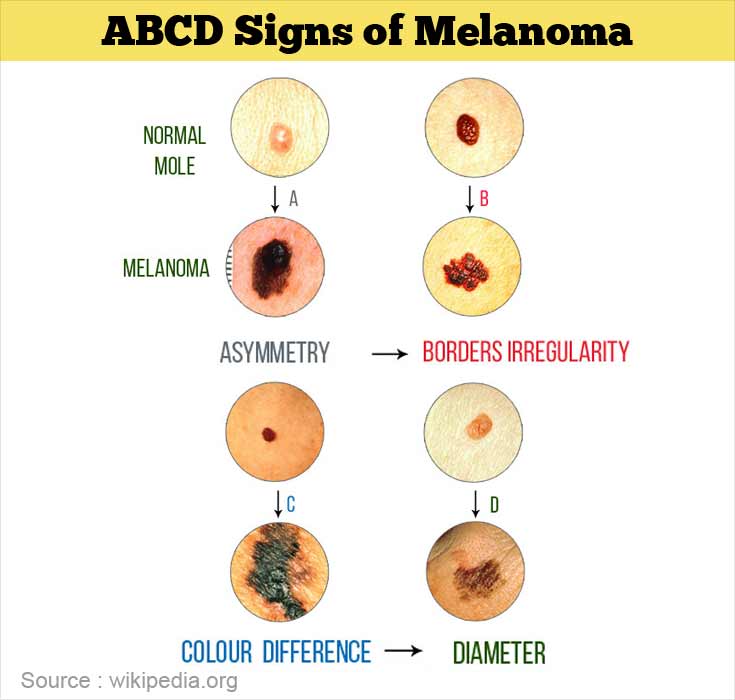
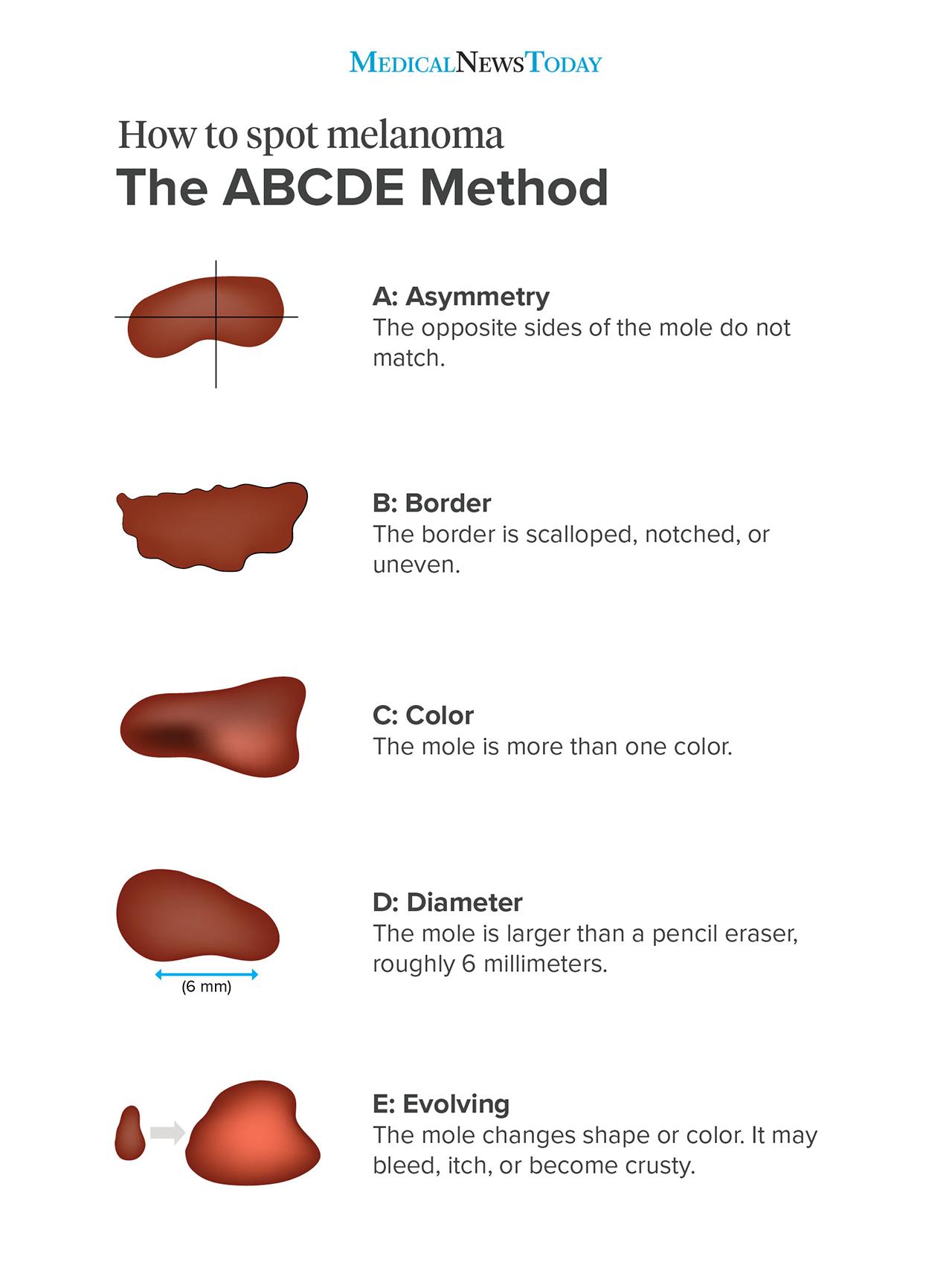
The ABCDEs of Melanoma (H1)
5. Asymmetry (H2)
Moles or growths that are not symmetrical could be a red flag. If one half of a mole looks different from the other half, consult a dermatologist.
6. Border Irregularity (H2)
Moles with irregular, notched, or scalloped borders are often indicative of melanoma. Check your moles for these irregularities.
7. Color Variation (H2)
Moles with multiple colors or an uneven distribution of color should be examined. Shades of brown, black, and even red or white can signal melanoma.
8. Diameter (H2)
A mole larger than the size of a pencil eraser (approximately 6mm) may be a cause for concern.
9. Evolution (H2)
Pay attention to moles that evolve or change over time. This includes changes in size, shape, color, or elevation.
Other Warning Signs (H1)
10. Itchiness or Pain (H2)
Moles or skin growths that become itchy, painful, or tender should be evaluated promptly.
11. Bleeding or Crusting (H2)
Any mole that bleeds, oozes, or develops a crust should not be ignored.
12. Swelling or Redness Beyond the Border (H2)
Melanoma may cause the skin around a mole to become swollen or red.
13. Satellite Moles (H2)
The presence of smaller moles surrounding a larger one could be indicative of melanoma.
Conclusion
Malignant melanoma is a serious condition that requires early detection and intervention. By being vigilant about these symptoms and signs, you can take proactive steps to protect your health. Remember that any changes in moles or the appearance of new ones warrant a visit to your dermatologist.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. Can melanoma occur in people with darker skin tones?
Yes, while it's less common, melanoma can affect individuals with all skin types, including those with darker skin.
2. Are all moles a sign of melanoma?
No, not all moles are cancerous. Many moles are benign. However, any changes in moles should be examined by a healthcare professional.
3. Can melanoma occur in areas not exposed to the sun?
Yes, melanoma can develop in areas of the body that are not regularly exposed to the sun, such as the soles of the feet or palms of the hands.
4. Is melanoma hereditary?
In some cases, there may be a genetic predisposition to melanoma. It's important to discuss your family history with a healthcare provider.
5. How is melanoma treated?
Treatment for melanoma typically involves surgical removal of the cancerous tissue. In more advanced cases, additional therapies such as radiation or immunotherapy may be required.
The development of a new pigmented or unusual looking growth on your skin.
The development of a new pigmented or unusual-looking growth on your skin is a potential sign that should not be ignored. These new growths, often referred to as "skin lesions" or "skin abnormalities," can vary in appearance and may indicate various skin conditions, including skin cancer, with malignant melanoma being one of the most concerning possibilities.
Here are some key points to understand about new pigmented or unusual-looking skin growths:
1. Appearance:
New growths on the skin can take on various appearances. They may appear as moles, freckles, raised bumps, flat patches, or even sores that do not heal.
Pay close attention to the color, shape, and size of these growths. Changes in these characteristics may be significant.
2. Pigmentation:
The presence of pigmentation, especially in the form of dark or multicolored areas within the growth, can be a warning sign. Such pigmentation can indicate the presence of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color, and may be associated with melanoma.
3. Evolution:
One critical aspect to watch for is how these new growths evolve over time. Changes in size, shape, color, or texture can be red flags.
Any growth that undergoes rapid changes or becomes irregular should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
4. Itching or Discomfort:
New growths that become itchy, painful, or cause discomfort can be concerning. These symptoms may indicate an underlying issue that requires medical attention.
5. Location:
The location of the new growth can also provide clues. Melanoma can develop anywhere on the body, including areas not typically exposed to the sun, such as the soles of the feet or the palms of the hands.
6. Risk Factors:
Consider your personal risk factors, such as a family history of skin cancer, a history of severe sunburns, or excessive UV exposure, as they can increase your susceptibility to skin cancer.
7. Early Detection:
Early detection of any suspicious skin growth is crucial. Regular self-examinations and professional skin checks by a dermatologist can help identify potential issues early on.
8. Seeking Medical Evaluation:
If you notice a new, pigmented, or unusual-looking skin growth that concerns you, it is advisable to seek medical evaluation promptly.
Dermatologists are experts in assessing skin conditions and can perform biopsies or other diagnostic tests if necessary to determine the nature of the growth.
In summary, the development of a new pigmented or unusual-looking growth on your skin should be taken seriously. While not all new growths are cancerous, it is essential to be vigilant and seek professional evaluation if you have any concerns. Early detection and timely medical intervention can make a significant difference in the outcome, especially when it comes to conditions like malignant melanoma.

Malignant melanoma symptoms and signs. Melanoma is a type of skin cancer that forms in pigment forming cells melanocytes. Melanoma is a type of skin cancer that forms in pigment forming cells melanocytes. Another important sign is a spot that looks different from all of the other spots on your skin known as the ugly duckling sign.
Melanoma is a skin cancer that can show up on the skin in many ways. The most important warning sign of melanoma is a new spot on the skin or a spot that is changing in size shape or color. What are the signs and symptoms of melanoma.
Educating patients regarding melanoma warning signs. A mole or melanocytic nevus is a benign tumor of these pigment forming cells melanoma is the most serious type of skin cancerrarely melanomas can be found in other areas of the body that contain pigment forming cells including the eye the tissues around the brain and spinal cord or the digestive tract. The first melanoma signs and symptoms often are.
Learn the symptoms treatment and outlook for metastatic melanoma. Nouri k et al. Approved by the cancernet editorial board 012019.
Later diagnosis often requires additional treatment such as chemotherapy which carries a higher risk of side effects. Melanoma symptoms and signs. Metastatic melanoma occurs when cancer spreads from a skin tumor to other parts of your body.
It can look like a. Learn what are the early warning signs of melanoma. But size is not a sure sign of melanoma.
Use the menu to see other pages. You will find out more about body changes and other things that can signal a problem that may need medical care. When signs of melanoma are commonly known and concerning lesions may be able to be picked up at an earlier stage cure rates are much higher and often only local removal of the lesion itself is required.
The first sign of a melanoma is often a new mole or a change in the appearance of an existing mole. A mole or melanocytic nevus is a benign tumor of these pigment forming cells melanoma is the most serious type of skin cancer. Normal moles are generally round or oval with a smooth edge and usually no bigger than 6mm in diameter.
Mcgraw hill medical china. Cancerous malignant moles vary greatly in appearance. A change in an existing mole.
Some may show all of the changes listed above while others may have only one or two unusual characteristics. Symptoms and signs of melanoma include new spots on the skin or a change in size shape or color of an existing mole.
Melanoma Symptoms And Signs Extensive Guide

Pin On Health

Malignant Melanoma
Melanoma Causes Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Prevention

Spotting Early Signs Of Melanoma Everyday Health
Overview Of Melanoma
Skin Cancer Symptoms Types And Warning Signs

Symptoms Of Advanced Melanoma Melanoma Cancer Research Uk